
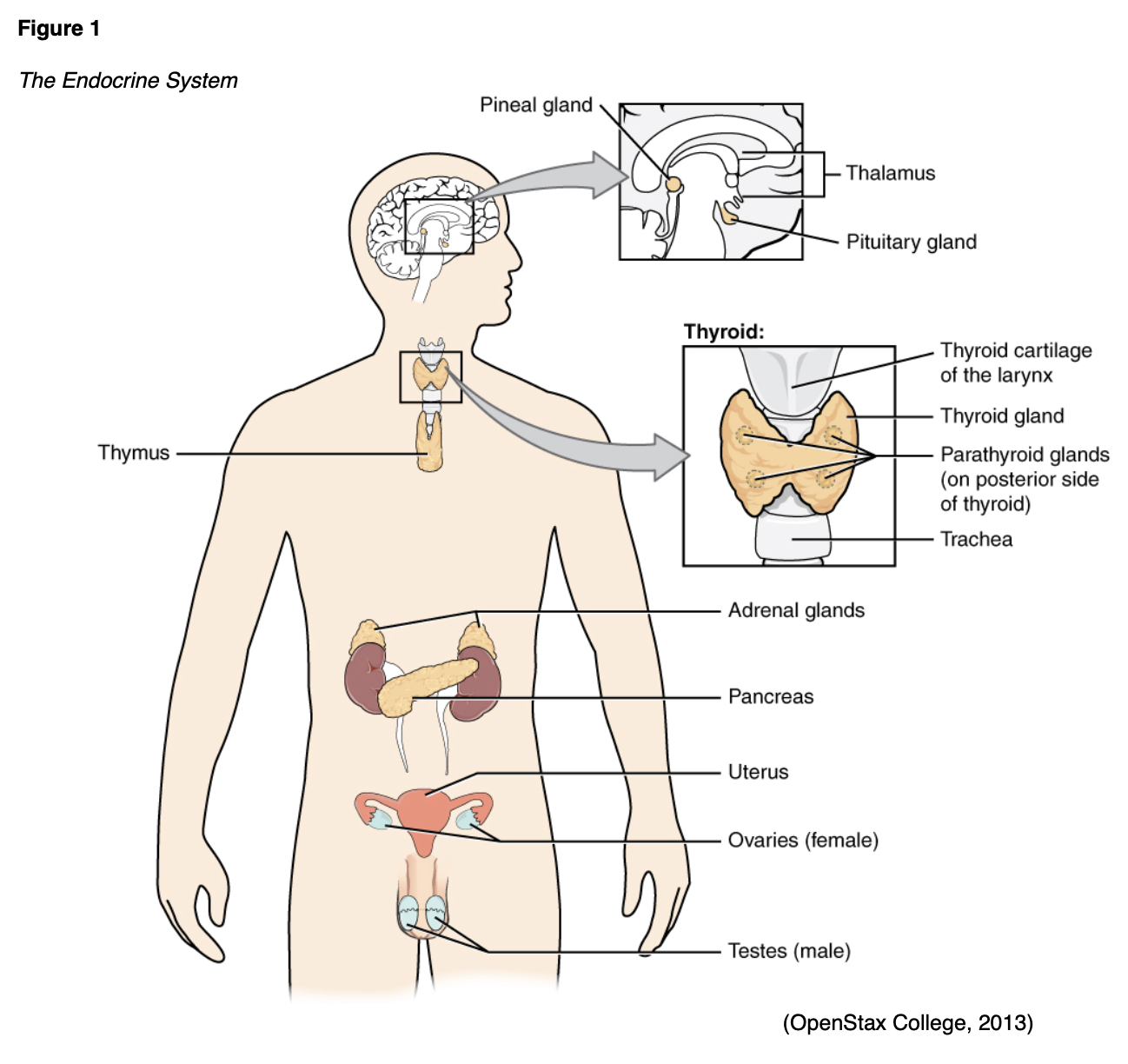
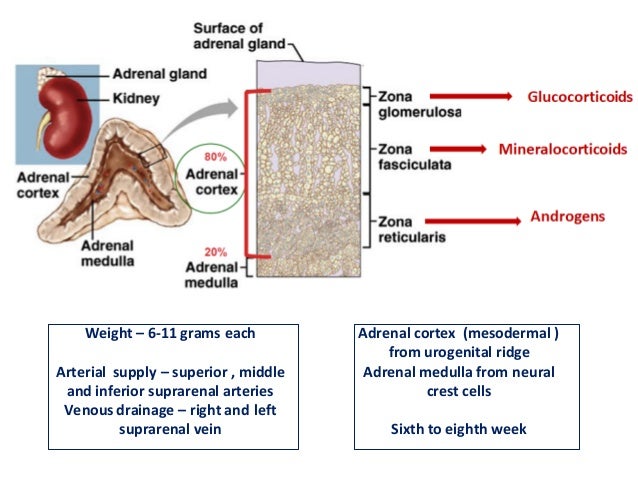
This approach opens the possibility of characterizing the neurobiological underpinnings of ADHD (and associated cognitive dysfunction) and its treatment by targeting specific neural circuits. Recent positron emission tomography evidence has highlighted the utility of quantifying DA markers, at baseline or following drug administration, in striatal subregions governed by differential cortical connectivity. Herein, we review and discuss the present state of knowledge regarding the roles of dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline in the regulation of corticostriatal circuits, with a focus on the molecular neuroimaging literature (both in ADHD patients and in healthy subjects). However, the precise prefrontal cortical and subcortical mechanisms by which these agents exert their therapeutic effects remain to be fully specified. Medications used in the treatment of ADHD (including methylphenidate, dextroamphetamine and atomoxetine) act to increase brain catecholamine levels. Through neuromodulatory influences over fronto-striato-cerebellar circuits, dopamine and noradrenaline play important roles in high-level executive functions often reported to be impaired in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
